Categories In Statistics
There are two main categories in Statistics, namely:
- Descriptive Statistics
- Inferential Statistics
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive Statistics uses the data to provide descriptions of the population, either through numerical calculations or graphs or tables.
Descriptive Statistics helps organize data and focuses on the characteristics of data providing parameters.
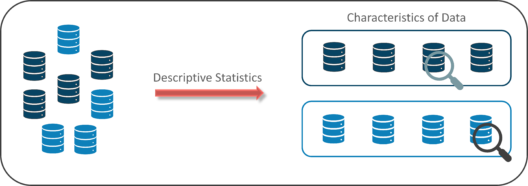
Suppose you want to study the average height of students in a classroom, in descriptive statistics you would record the heights of all students in the class and then you would find out the maximum, minimum and average height of the class.

Inferential Statistics
Inferential Statistics makes inferences and predictions about a population based on a sample of data taken from the population in question.
Inferential statistics generalizes a large data set and applies probability to arrive at a conclusion. It allows you to infer parameters of the population based on sample stats and build models on it.
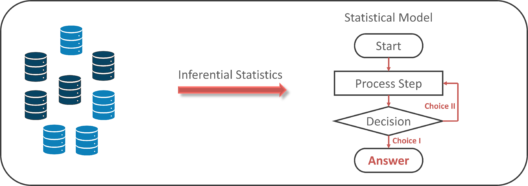
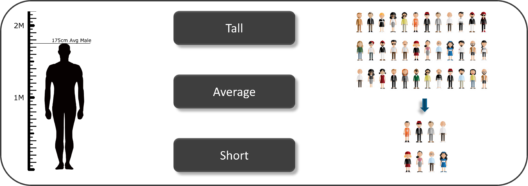
So, if we consider the same example of finding the average height of students in a class, in Inferential Statistics, you will take a sample set of the class, which is basically a few people from the entire class. You already have had grouped the class into tall, average and short. In this method, you basically build a statistical model and expand it for the entire population in the class.
Now let's focus our attention on Descriptive Statistics and see how it can be used to solve analytical problems.