Basics
Solar electric systems convert the sun's light energy into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells. A solar cell, made from two layers of semi conducting material, usually silicon, creates an electric field across the layers when light shines on it. The amount of energy that can be produced is directly dependent on the intensity of the sunshine. Assemblies of cells are used to make solar panels, also called solar modules. Modules or panels together constitute photovoltaic arrays.
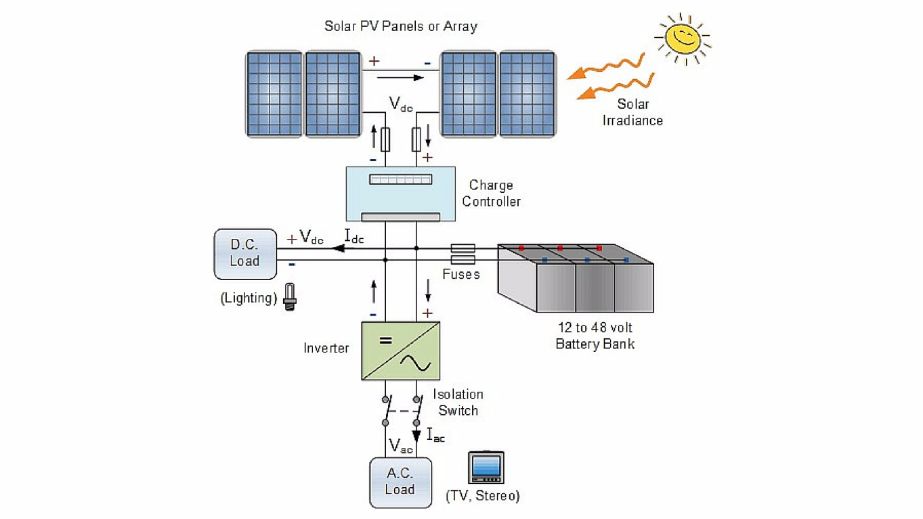
Solar PV systems can be connected to the grid or can work as isolated systems for the use of single households or institutions. An isolated solar power system is referred to as an off grid or stand alone system and, involves the use of storage batteries. The batteries store the excess energy generated by the PV array and, in it turn, provide electricity to the connected load when the sun is not available.
Off grid PV systems are more complex than grid connected systems:
- A charge controller is used so that the batteries are not damaged by overcharging or excessive discharge.
- When the loads are not DC, then, an inverter is used to convert DC power from the batteries into AC.
In case the sun is not fully available for a string of days or the users draw more power than what the batteries should provide, the system might go down. To avoid this, an off grid system is often backed up by a diesel generator to enable continuous charge to the battery bank.