Systems
What are the SYSTEMS in a Building?
- MECHANICALS (HVAC) - The fresh air distribution and exhaust air collection is handled by the Heating, Ventilation and Cooling system. This system can include boilers, furnaces, fans, HRV/ERVs and long lines of ductwork. In a building, there can be a specific room where boilers and heating / cooling equipment are placed, usually close to where electrical and/or fuel supply lines come into the structure. The ductwork will be behind walls and ceilings, or in a special cavity called a chase.
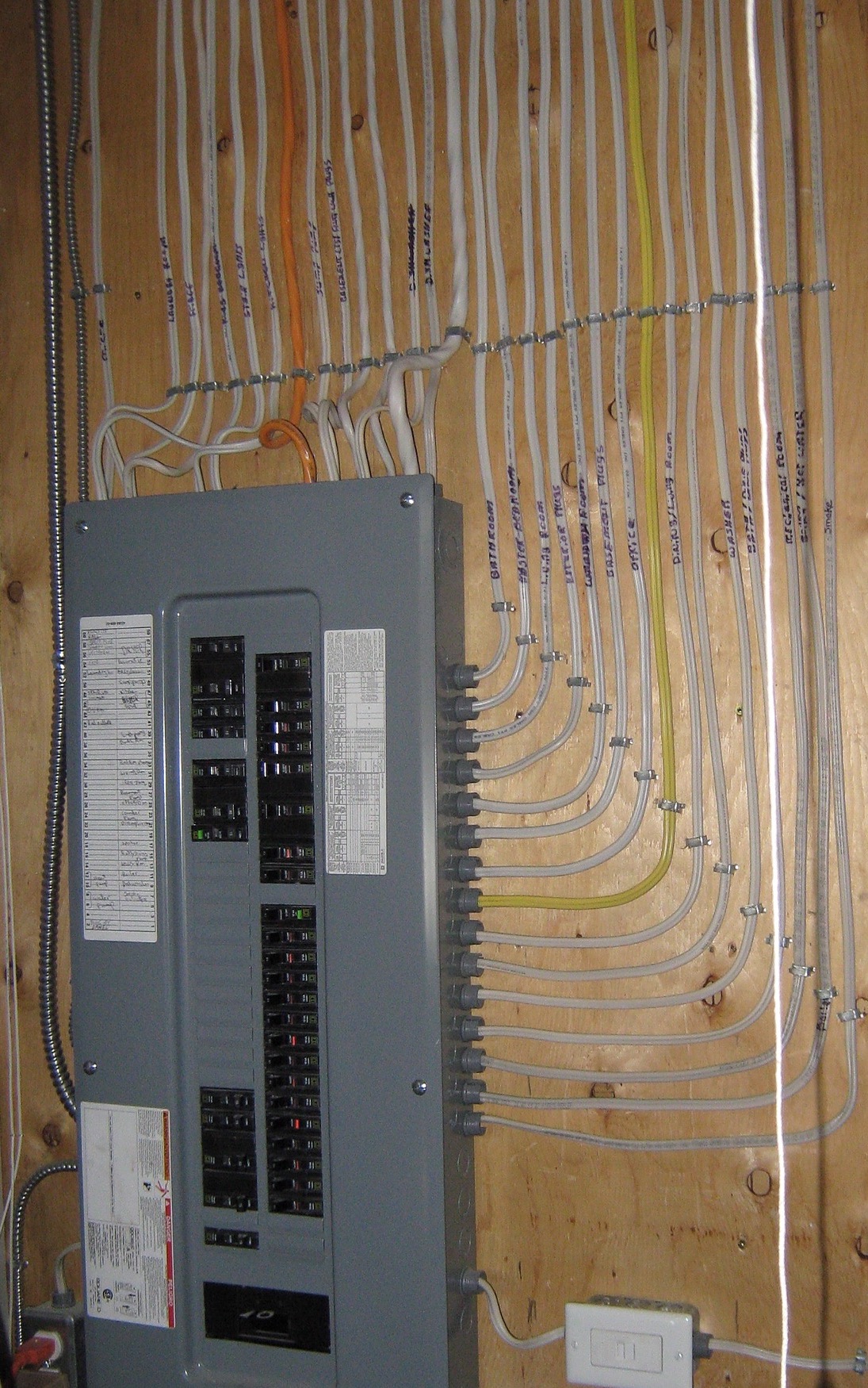
- POWER & LIGHTING - This system involves all of the panels, wires, outlets and lighting fixtures in a building. Power is drawn from the grid, brought into a panel (or panels) and distributed throughout on breakers and kilometres of wiring. For safety reasons, this system is kept behind the walls, ceilings and floors, accessible in dedicated rooms or in access ways called conduits.
- MEANS OF EGRESS - This part of of a building is more simply described as 'how people get in, get out and get around'. Some common means of egress are doors, windows, hallways, elevators and stairways. Egress is closely tied to the fire safety of a building.
- FIRE ALARMS & SUPPRESSION - In hallways, stair wells and in apartment units, there will be alarm systems and sprinklers in case of fires. The alarm pulls, bells and sprinkler pumps will be tied into emergency electricity (if the power goes out). This system serves to allow occupants to get OUT of a building in a fire and to alert responders via network connection.
- DATA & TELEPHONE NETWORK - Although the provision of internet and/or phone is handled by independent companies, many buildings will have chases or conduits specifically for the wiring and cables needed for this network. Also, many high rise buildings will have towers on top to host cellular, wireless internet, radio and TV equipment.
In order to meet more modern understanding and requirements of indoor air quality, most buildings use devices called HRVs or ERVs:
- HRV - Heat Recovery Ventilator. This box is integrated with the HVAC system, operating to recover the heat from exhaust air and transferring it to incoming, cooler fresh air.
- ERV - Energy Recovery Ventilator. Much like an HRV, with the added benefit of helping to moderate humidity by removing moisture from outgoing exhaust air and giving it back to incoming fresh air.
These devices can be very large, roof top units, built to serve an entire building OR boxes small enough to fit in a closet to serve only one apartment.