The Role of Insulation & Heat Loss
Insulation divides air space to reduce heat transfer by convection and reduces heat transfer by radiation.
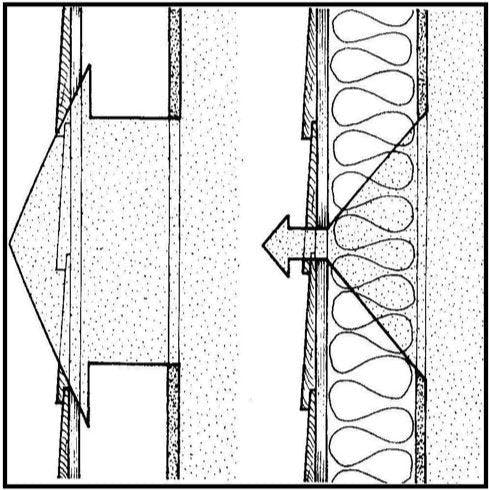
Heat always moves from warm to cool by conduction, convection and radiation. Still air does not conduct heat well but, in a large space, such as a wall cavity, heat is lost by convection and radiation. Insulation forms the most significant piece of the Thermal Control Layer by dividing the air space into many small pockets of still air; this inhibits heat transfer by convection. At the same time, radiation across the space is reduced. This Thermal Control Layer is often referred to as the Thermal Barrier.
Insulation Requirements
Continuous insulation contributes to high-performance assemblies. While the Building Code lists minimum insulation requirements for energy efficiency there are other codes and standards for insulation requirements including:
- NRCan's ERS System rates the energy efficiency of houses, including their insulation and airtightness qualities
- R-2000 is performance based, no prescriptive insulation requirements
- ENERGY STAR, NetZero and NetZero Ready, and Novoclimat 2.0 all require the home to meet or exceed the local Building Code requirements for minimum insulation requirements