Soil Gas Control
Prior to any DER project, measures must be taken to prevent entry of soil gases into the home. Radon is a soil gas with significant and well-documented health risks. Air moving through soil also carries significant moisture and may carry other contaminants such as mold spores, herbicides, pesticides, methane, etc.
As a minimum soil gas control measure, cracks and holes in the foundation walls and basement slab must be sealed. Because of the need for soil gas control, it is important that any penetrations made through ground-contact assemblies (slabs and foundation walls) are sealed. Sump pits must have airtight and gasketed covers.
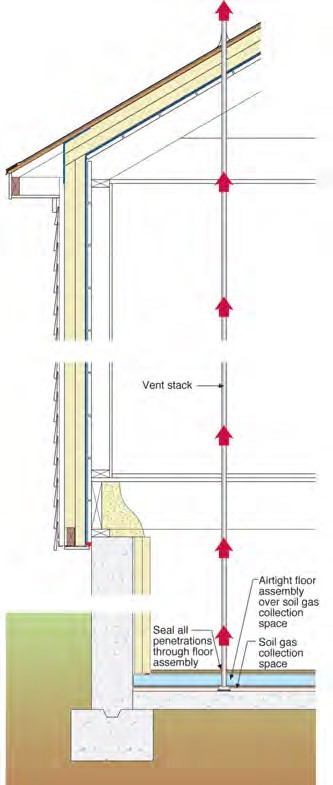
Implementation of a soil gas venting system is strongly recommended. Any significant work to the roof or basement/crawlspace provides an opportunity to establish such a system.
A soil gas venting system essentially provides the soil gas with an express lane bypass to the outside so that it does not move through the indoor living space. If needed, a fan can be added to the vent pipe to actively move soil gases from beneath the basement floor to the outside.
Soil gas venting system
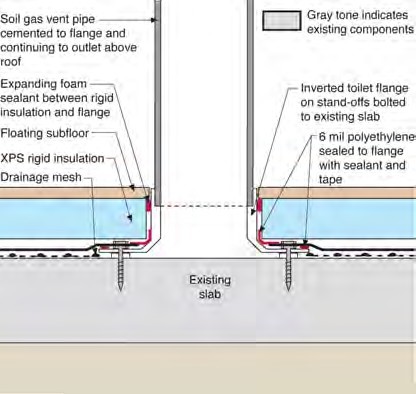
A retrofit soil gas venting system works as follows:
- A soil gas collection space is established. This can be
- a drainage space created by a dimple mat or drainage mesh above an existing slab, or
- a sump pit connected to gravelly or sandy soil below an existing slab.
- The soil gas collection space must be thoroughly air sealed from the living space.
- The soil gas collection space is passively depressurized by passive stack action of a warm vent stack located inside heated space for as great a vertical distance as practical.
- The vent stack extends from the soil gas collection space to an outlet at the roof with as few offsets and elbows as possible. Avoid 90-degree elbows. Sweeps are preferred if turns are needed.
- The vent stack extends through the roof at least 2 feet above the roof. A screened rain cap is provided at the termination to prevent rain entry or the obstruction of the outlet by nesting animals.
- If the vent stack extends through an unconditioned attic, insulate the stack in this space to control condensation inside the pipe.
For additional information on soil gas control consult Build Radon Out produced by the US EPA and available for download at http://www.epa.gov/radon/pubs/#index4.