Insulating Around Obstacles
General
It is difficult to describe every situation that will be encountered by the insulation installer. In general, however, the installer should be guided by the need to reduce heat flow around or through obstructions and to protect mechanical systems.
Electrical
Junction boxes for wall switches and convenience outlets at outside walls should be insulated between the rear of the box and the sheathing. Place insulation behind the junction box and cut insulation to fit snugly around it. (See Figure 26.)
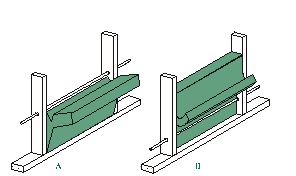
Where electrical wiring passes through a stud cavity and is located close to the inside wall surface,insulation should be pressed behind the wiring. When the wiring is in the center of the cavity,either a shallow cut in the insulation may be used to allow the wiring to pass through the insulation or it may be split lengthwise and the wiring sandwiched within. (See Figure 27 A and B.)
Figure 26
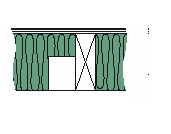
figure 27
The National Electrical Code contains the following recessed lighting fixture requirement:"Thermal insulation shall not be installed within 3 inches of the recessed fixture enclosure,wiring compartment or ballast and shall not be so installed above the fixture as to entrap heat and prevent the free circulation of air unless the fixture is otherwise approved for the purpose.''The requirements of the NEC must be followed.
Plumbing
To have the optimum thermal performance of insulation in the building envelope, it is important to minimize obstructions such as plumbing vent pipes and air ducts (see below). Additionally, placing plumbing pipes that contain standing water in the building envelope should be avoided when possible. These include waste traps and water supply lines. When it is necessary to locate these items within the building envelope, the insulation should be installed in contact with the obstruction to prevent excessive voids. If the insulation has a kraft type vapor retarder, it should be placed in substantial contact with the gypsum board. (See Figure 28.)
Figure 28
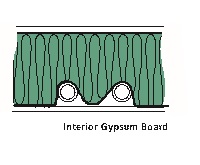
Air Ducts
Air ducts in an unconditioned space must be insulated. Insulated air ducts contribute to the home's overall indoor environment by delivering heated and cooled air at design temperatures and absorbing noise generated by central air conditioning equipment,air rush and cross-talk. In addition,insulated air ducts control the heat loss or gain through the air duct walls.
If an air duct runs through an unconditioned space such as an attic or a side wall,it should either insulated with duct wrap or batt insulation should be applied between the duct and the exterior wall sheathing.
Openings Through Building Sections
Where pipes, wiring, or ductwork penetrate a building section, any openings should be sealed to prevent air infiltration.