States of Matter
There are three states of matter: solid, liquid and gas. A solid will keep its shape with or without a container and has a fixed volume. A liquid has a fixed volume but will assume the shape of its container. A gas will expand and disperse over time; thus it does not have a fixed volume or shape without a container.
Heat of Fusion and Heat of Vaporization
As solid or liquid fuels are exposed to heat, they absorb energy. The molecules increase in temperature depending on the specific heat capacity of the material, and can absorb enough energy from a fire to turn into vapour before they mix with air and burn.
When a solid heats and reaches its melting point, it absorbs additional energy, known as the "latent heat of fusion," until the solid material turns into a liquid. With additional heating, the temperature of the liquid increases in temperature until it reaches its boiling temperature, the highest temperature at which it can exist in liquid form at a particular atmospheric pressure. How much heat is required to increase the temperature of a unit mass of liquid (or any other material) by one degree in temperature is determined by the specific heat capacity of that material and designated as cP.
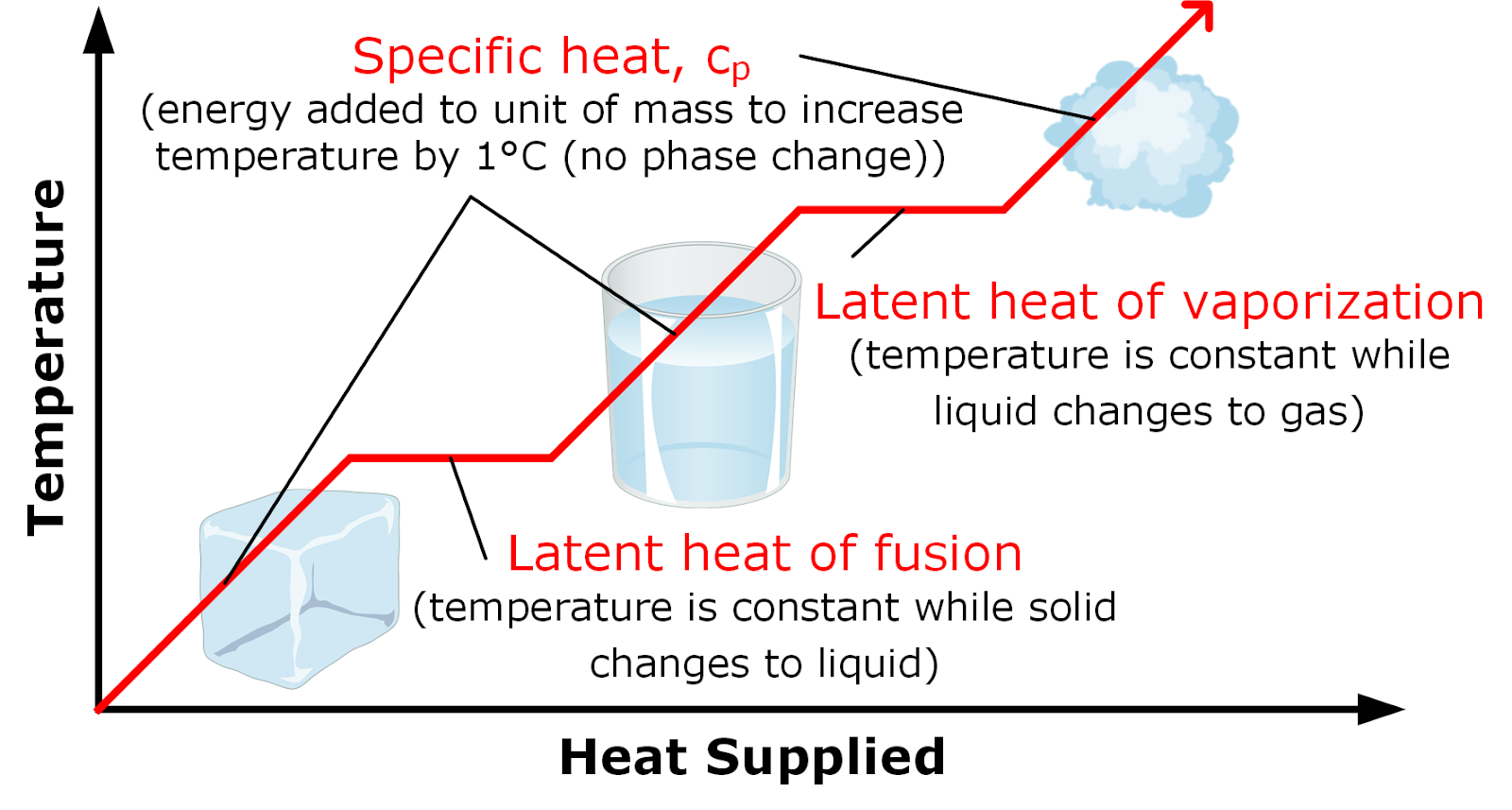
At the boiling point, the liquid undergoes a phase change from liquid to gas in a process called evaporation. During the phase change, the liquid will not increase in temperature, because all of the heat that is added is used (absorbed) to overcome the latent heat of vaporization (energy added into the liquid to change the phase of the material from a liquid to a gas).
The higher the specific heat capacity and/or latent heat of vaporization of a material, the more energy must be absorbed by a given mass of material for it to increase in temperature and become a gas. This is also a key part of why water is such an effective cooling agent when applied correctly to a heated fire environment. Water has a very high heat capacity as well as a relatively high latent heat of vaporization value. This means that water at ambient temperature first has to absorb heat to get to its boiling temperature (100°C). It then absorbs more heat from the environment as it evaporates and turns into steam.
|
Knowledge Check True or False: Is fire a chemical reaction? Is fire an endothermic or exothermic reaction? What are the two broad categories of energy? What is a Joule? What is a calorie? Are heat and temperature the same thing? What is specific heat capacity? What is the heat of fusion? What is the heat of vaporization? |